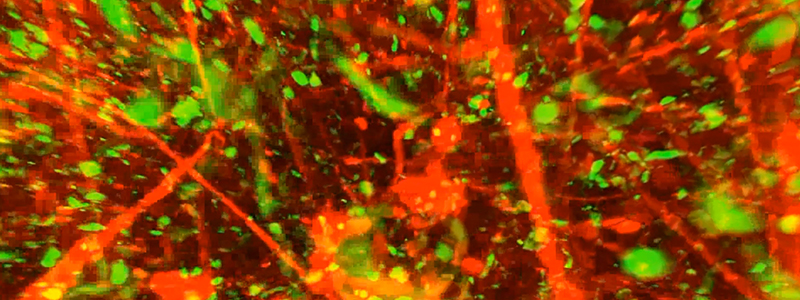
Kunie Ando, Benoit Delatour and Charles Duyckaerts, in the team of Marie-Claude Potier and Stéphane Haïk at the Institut du Cerveau – ICM, used for the first time in Alzheimer disease patients a method, called CLARITY, which permits three-dimensional visualization of the inside of a human brain.
With 860000 persons in France and 35 million worldwide that suffer from Alzheimer type dementia, this disease is at the centre of our preoccupations.
It is characterized by the progressive decline of several cognitive functions, resulting from the concomitant progression of two types of lesions: on the one hand, the abnormal accumulation outside neurons of a protein known as beta-amyloid peptide that leads to the formation of “amyloid plaques” also called “senile plaques;” on the other hand, the abnormal accumulation of the TAU protein inside neurons leading to neurofibrillary degeneration, synonymous with cognitive deterioration.
Thanks to the CLARITY technique, the team visualized these lesions and studied the organization of the brain in patients with Alzheimer disease. Post-mortem brain samples were furnished by the Brain Bank of the Salpêtrière GIENeuroCEB, financed by the patient associations France Alzheimer, France Parkinson, ARSEP and CSC.
This technique, developed at Stanford, renders the brain transparent while leaving its internal structure intact. It consists of replacing the lipids (fat molecules) by a transparent gel. The researchers could then visualize certain molecules with fluorescent probes and observe the organization of the senile plaques, the trajectories of axons and neurofibrillary degeneration in a post-mortem sample.
This technique is very useful for visualizing in three dimensions the distribution in the brain of the lesions caused by the disease and provides precious information on the structure of the neuronal projections surrounding these lesions.
Référence
Ando K, Laborde Q, Lazar A, Godefroy D, Youssef I, Amar M, Pooler A, Potier MC, Delatour B, Duyckaerts C. Inside Alzheimer brain with CLARITY: senile plaques, neurofibrillary tangles and axons in 3-D. Acta Neuropathol. 2014 Sep;128(3):457-9. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1322-y. Epub 2014 Jul 29.